Free Stock Trading Course
Lesson One
Basic knowledge of stocks
Market operation principle / Market trading rules
What is the Stock Market?
The stock market has two main functions. Firstly, it provides capital for listed companies. Companies can raise a large amount of funds through the stock market to accelerate successful startups, expand existing businesses, integrate operations, and repay debts.
The second purpose of the stock market is to give investors (i.e., those who purchase stocks) the opportunity to share the profits of listed companies. Investors can profit from stock purchases in two ways. Some stocks pay dividends regularly. Another way for investors to profit from purchasing stocks is that if the stock price rises from the purchase price, investors can sell the stocks to make a profit and earn the difference. For example, if an investor purchases stocks of a certain company at $10 per share and the stock price subsequently rises to $15 per share, the investor can make a 50% investment profit by selling the stocks..
The stock market is essentially a platform for investors to buy and sell stocks of listed companies. These stocks represent the ownership of the companies. Investors who purchase stocks become shareholders and thus have the right to receive part of the company's dividends and earn profits by buying and selling stocks through the difference.
What is a stock exchange?
Stock exchanges are the central locations for buying and selling stocks. There are large exchanges all over the world, such as the London Stock Exchange, the Tokyo Stock Exchange and the Shanghai Stock Exchange. Each exchange has its own internal rules, and investors abide by different national and local laws. These are aimed at ensuring fair trading behaviors and making investors confident in trading there. They also provide transparency in the trading process and offer real-time information on stock prices. This is why you can easily find the latest stock prices and trend synchronizations on almost any financial news website. Currently, the United States has the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) located in New York City, as well as the Nasdaq Stock Exchange, which is one of the largest and most renowned stock exchanges in the world. Including the Over-the-Counter Market (OTC)

The three major indices of the stock market (the barometers of the stock market)
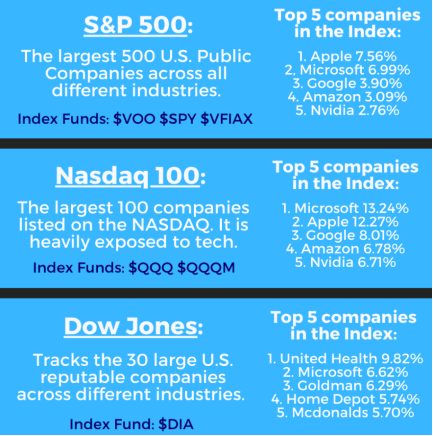
When financial news flashes on your screen, three names are always at the top: the Dow Jones Industrial Average, the S & P 500, and the Nasdaq Composite Index. But have you ever wondered why these particular indexes dominate financial discussions, influence investor sentiment, and often become synonymous with the entire U. S. stock market? The three indexes are so popular, not only because of their long history, but also because they can quickly measure different aspects of the U. S. economy. Each index tells a unique story: the Dow focuses on blue-chip industries, the S & P 500 provides broader market representation, and the Nasdaq holds the pulse of the technology sector. Their collective influence extends far beyond Wall Street, affecting everything from retirement savings to global economic policy. When people refer to stocks up or down, they usually refer to one of the major market indexes. The Dow's focus on 30 blue-chip companies quickly reflects the state of the U. S. industrial giants. The oldest of the three, the Dow is historic and often makes headlines.
1. The S & P 500 index. Often known as the S & P 500, the index reflects the overall picture of the 500 largest listed companies in the US and provides a more comprehensive picture of the US economy.
2. The Nasdaq Composite Index. The Nasdaq Composite index, which leans heavily toward technology companies, is seen as a barometer of innovation and the overall situation in the technology industry.
3. The Dow Jones Industrial Average. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) includes the stocks of the 30 largest and most influential companies in the country.
According to the overall situation of the index can understand the recent trend of the stock market, including which index you buy stocks belong to the index also need to pay attention to the situation of the stock, usually fall with the index fell, this is the stock affected by the market, while the index rose, stocks will have a certain probability is pushed up.
4. How has the stock price be determined
Stock prices are driven by investor supply and demand, and by corporate performance, market sentiment and broader economic factors. While fundamentals such as earnings and growth are crucial, external factors such as investor psychology and global events can also lead to significant changes in short-term prices.
5. Bull markets and bear markets
The bull and bear markets are opposite trends in the stock market, characterized by stock price rises and falls, respectively. These terms are used to describe investor sentiment, the overall market direction, and the performance of investments over time. A bull market is a rising stock price or an expected rising stock price. Bull markets are often associated with strong investor confidence, strong economic growth, and increased investment activity. In a bull market, stocks are more likely to profit and are more profitable. A bear market is a falling stock price or an expected fall. Bear markets are often driven by fear and pessimism, and investors expect economic conditions to deteriorate, causing them to sell stocks. So in a bear market, stocks are prone to fall and cause large losses, but investors can make short positions to make down profits. Stock trading can be earned either by buying up or down, depending on whether your stock account supports short selling rights.

6. Stock market trading rules:
When will the stock market be open?
9:30 am to 4 pm Eastern time (ET).
What is pre-market trading and after-hours trading
Pre-and after-hours trading is trading outside of standard trading hours (9:30 a. m. to 4:00 p. m., Eastern time). These periods allow investors to react to news and events outside of normal trading hours, providing greater flexibility for trading.
What is the pre-market trading
On most U. S. exchanges, premarket trading typically occurs between 4:00 a. m. and 9:30 a. m. EDT, but some brokers may limit trading to certain periods of that period.
During this period, investors may buy or sell securities based on news, earnings reports, or other events occurring before the market opening. For example, important announcements about earnings or mergers are usually made early in the morning.
This period is generally lower and more volatile, which can lead to wider bid-sell spreads (the difference between the price the buyer is willing to pay and the price the seller is willing to accept). These conditions could increase premarket trading risk, especially for less liquid stocks.
What is the after-hours trading
After-hours trading (also known as after-hours trading) usually occurs from 4:00 p. m. to 8:00 p. m. EDT. This period allows investors to react to news releases after the market closes, such as earnings reports, economic data, or important company announcements.
As with premarket trading, after-hours trading is typically less liquid and more volatile. This could lead to higher price volatility and wider bid-sell spreads. Some stocks may have very limited after-hours trading activity, while others, especially large-cap or stocks with breaking news, may be more active.
Trading outside of normal trading hours is good for quick response events, but investors should be aware that the risk in these trading periods may be increased and that the pricing may be less favorable.
Can you place a buy order during the pre-market trading session?
Pre-hours and after-hours trading is a useful tool for experienced investors looking to respond to the news outside of normal trading hours. Investors can place orders to buy and sell shares in premarket hours, for major U. S. exchanges, usually 4:00 a. m. to 9:30 a. m. ET on the New York Stock Exchange and Nasdaq. However, these times may vary from broker to broker, and not all brokers provide access to the entire pre-market period. Because of these risks of low liquidity and high volatility in the early days, traders should be cautious.
Stock market trading unit
the smallest trading unit is 1 share.
Stock market trading cycle
Stock market trading cycle: intra-day trading is a trading model. day trade refers to a client buying or selling a position in a stock or stock option on the same trading day. Day trading is also commonly known as T + 0 trades. Short-term trading is usually 3-5 days, medium-and long-term trading is usually more than 2 weeks, and long-term trading is usually more than 3 months.
Stock market regulator
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulates the market (including investors and various financial institutions, brokerages and banks) to ensure that the market is fair, orderly and transparent. The SEC requires listed companies to regularly disclose their financial reports and major events to protect investors from fraud and unfair trading practices.
This concludes the Basic knowledge of stocks. Please use the menu below to navigate to the lesson of your choice.

